Affective Computing. Affective computing is a field of study within computer science and artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on the design and development of systems and devices capable of recognizing, interpreting, and responding to human emotions. The term was coined by Rosalind Picard in her 1995 paper, and she later expanded on the concept in her 1997 book titled “Affective Computing.
One of the most important component of affective computing is Emotion Recognition which involves using various sensors, algorithms, and data analysis techniques to detect and interpret emotional cues from humans. These cues can be gathered from: Physiological signals (measuring heart rate, skin conductance, and other biometric data); Facial expressions( using computer vision techniques to analyze facial movements); Voice tone and speech patterns (analyzing variations in pitch, speed, and other vocal features); Body language( Interpreting gestures, posture, and movements) …
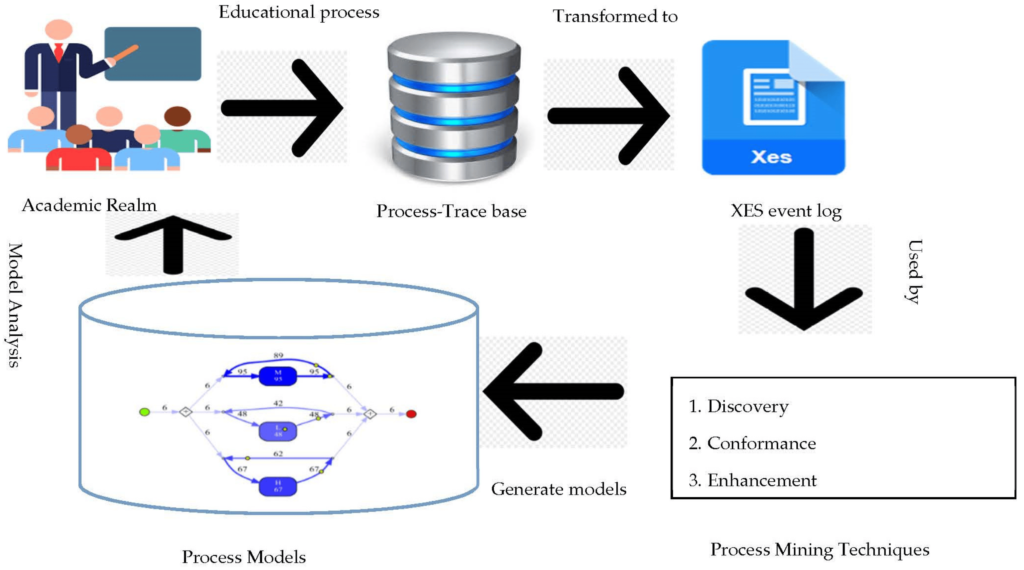
Process mining is a technique in data science that analyzes business processes based on event logs. It involves extracting knowledge from event logs readily available in today’s information systems to understand and improve business processes. The goal of process mining is to bridge the gap between traditional model-driven process analysis (such as Business Process Management) and data-driven analysis techniques like machine learning and data mining.
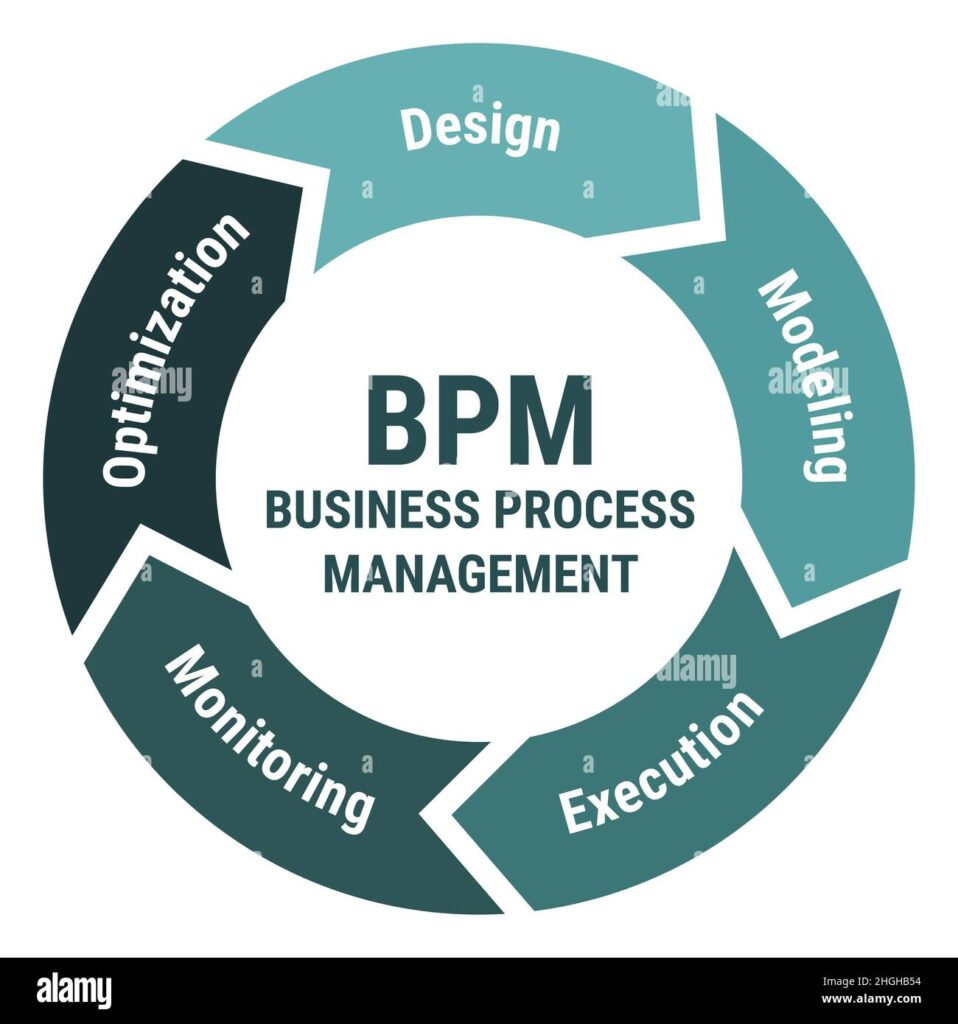
Business Process Management (BPM) – is a systematic approach to improving an organization’s business processes. BPM focuses on analyzing, modeling, optimizing, and automating processes to increase efficiency, reduce costs, enhance productivity, and ensure compliance with regulations. It is a holistic management discipline that aligns business processes with an organization’s goals and strategies. Key components of BPM include Process Design (defining and mapping out the business processes within an organization); Process Modeling (visualizing the process flow, identifying potential bottlenecks, and testing changes before implementation); Process Execution (integrating the process with existing enterprise systems like ERP, CRM, or other specialized applications); Process Monitoring (racking the performance of business processes in real-time. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are used to measure effectiveness, efficiency, and complianc); Process optimization (liminating unnecessary steps, automating manual tasks, reallocating resources, or re-engineering the entire process) and Process automation (automating routine tasks to improve efficiency. Automation can reduce errors, lower costs, and speed up processes).
Petri Nets are a mathematical modeling language used to describe and analyze the flow of information or resources in systems, particularly those with concurrent, asynchronous, or distributed characteristics. They are a powerful tool for modeling, simulating, and analyzing processes in a variety of fields, including computer science, manufacturing, and communication systems.
